OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Pairs Trading Scanner [BackQuant]
Pairs Trading Scanner [BackQuant]
What it is
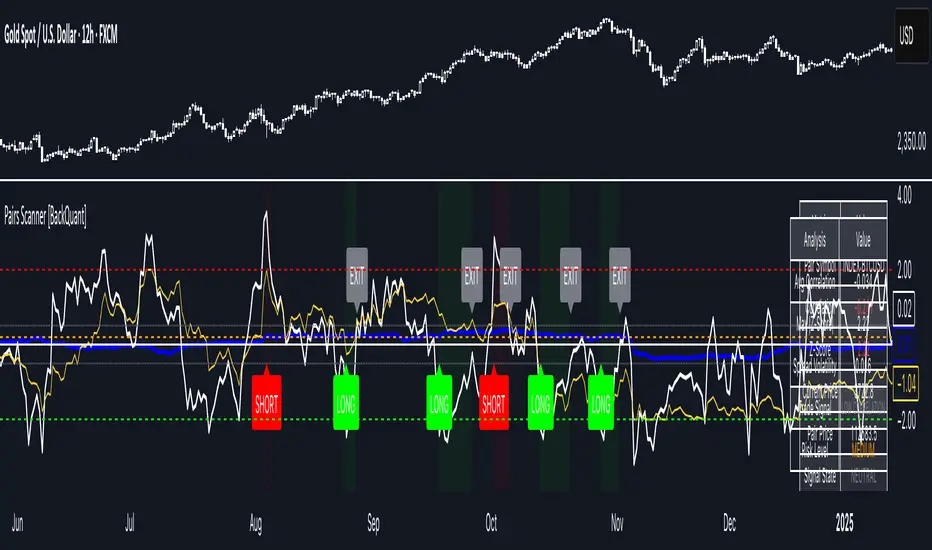
This scanner analyzes the relationship between your chart symbol and a chosen pair symbol in real time. It builds a normalized “spread” between them, tracks how tightly they move together (correlation), converts the spread into a Z-Score (how far from typical it is), and then prints clear LONG/SHORT/EXIT prompts plus an at-a-glance dashboard with the numbers that matter.
Why pairs at all?
How it works (plain English)
Core concepts (the three pillars)
What you’ll see on the chart
The two built-in dashboards
Statistics Table (top-right)
Analysis Table (bottom-right)
Signals logic (plain English)
A quick, repeatable workflow
Settings that matter (and why)
Choosing pairs (practical cheat sheet)
Reading the cues like a pro
Frequently asked (quick answers)
Field notes & patterns
Display controls at a glance
Alerts (ready to route to your workflow)
Final notes
The scanner is designed to keep you systematic: require relationship (correlation), quantify dislocation (Z-Score), act when stretched, stand down when it normalizes or the relationship degrades. It’s a full, visual loop for relative-value trading that stays out of your way when it should and gets loud only when the numbers line up.
What it is
This scanner analyzes the relationship between your chart symbol and a chosen pair symbol in real time. It builds a normalized “spread” between them, tracks how tightly they move together (correlation), converts the spread into a Z-Score (how far from typical it is), and then prints clear LONG/SHORT/EXIT prompts plus an at-a-glance dashboard with the numbers that matter.
Why pairs at all?
- Markets co-move. When two assets are statistically related, their relationship (the spread) tends to oscillate around a mean.
- Pairs trading doesn’t require calling overall market direction you trade the relative mispricing between two instruments.
- This scanner gives you a robust, visual way to find those dislocations, size their significance, and structure the trade.
How it works (plain English)
- Step 1 Pick a partner: Select the Pair Symbol to compare against your chart symbol. The tool fetches synchronized prices for both.
- Step 2 Build a spread: Choose a Spread Method that defines “relative value” (e.g., Log Spread, Price Ratio, Return Difference, Price Difference). Each lens highlights a different flavor of divergence.
- Step 3 Validate relationship: A rolling Correlation checks if the pair is moving together enough to be tradable. If correlation is weak, the scanner stands down.
- Step 4 Standardize & score: The spread is normalized (mean & variability over a lookback) to form a Z-Score. Large absolute Z means “stretched,” small means “near fair.”
- Step 5 Signals: When the Z-Score crosses user-defined thresholds with sufficient correlation, entries print:
LONG = long chart symbol / short pair symbol,
SHORT = short chart symbol / long pair symbol,
EXIT = mean reversion into the exit zone or correlation failure.
Core concepts (the three pillars)
- Spread Method Your definition of “distance” between the two series.
Guidance:Log Spread: Focuses on proportional differences; robust when prices live on different scales.
Price Ratio: Classic relative value; good when you care about “X per Y.”
Return Difference: Emphasizes recent performance gaps; nimble for momentum-to-mean plays.
Price Difference: Straight subtraction; intuitive for similar-scale assets (e.g., two ETFs).
- Correlation A rolling score of co-movement. The scanner requires it to be above your Min Correlation before acting, so you’re not trading random divergence.
- Z-Score “How abnormal is today’s spread?” Positive = chart richer than pair; negative = cheaper. Thresholds define entries/exits with transparent, statistical context.
What you’ll see on the chart
- Correlation plot (blue line) with a dashed Min Correlation guide. Above the line = green zone for signals; below = hands off.
- Z-Score plot (white line) with colored, dashed Entry bands and dotted Exit bands. Zero line for mean.
- Normalized spread (yellow) for a quick “shape read” of recent divergence swings.
- Signal markers:
LONG (green label) when Z < –Entry and corr OK,
SHORT (red label) when Z > +Entry and corr OK,
EXIT (gray label) when Z returns inside the Exit band or correlation drops below the floor.
- Background tint for active state (faint green for long-spread stance, faint red for short-spread stance).
The two built-in dashboards
Statistics Table (top-right)
- Pair Symbol Your chosen partner.
- Correlation Live value vs. your minimum.
- Z-Score How stretched the spread is now.
- Current / Pair Prices Real-time anchors.
- Signal State NEUTRAL / LONG / SHORT.
- Price Ratio Context for ratio-style setups.
Analysis Table (bottom-right)
- Avg Correlation Typical co-movement level over your window.
- Max |Z| The recent extremes of dislocation.
- Spread Volatility How “lively” the spread has been.
- Trade Signal A human-readable prompt (e.g., “LONG A / SHORT B” or “NO TRADE” / “LOW CORRELATION”).
- Risk Level LOW / MEDIUM / HIGH based on current stretch (absolute Z).
Signals logic (plain English)
- Entry (LONG): The spread is unusually negative (chart cheaper vs pair) and correlation is healthy. Expect mean reversion upward in the spread: long chart, short pair.
- Entry (SHORT): The spread is unusually positive (chart richer vs pair) and correlation is healthy. Expect mean reversion downward in the spread: short chart, long pair.
- Exit: The spread relaxes back toward normal (inside your exit band), or correlation deteriorates (relationship no longer trusted).
A quick, repeatable workflow
- 1) Choose your pair in context (same sector/theme or known macro link). Think: “Do these two plausibly co-move?”
- 2) Pick a spread lens that matches your narrative (ratio for relative value, returns for short-term performance gaps, etc.).
- 3) Confirm correlation is above your floor no corr, no trade.
- 4) Wait for a stretch (Z beyond Entry band) and a printed LONG/SHORT.
- 5) Manage to the mean (EXIT band) or correlation failure; let the scanners’ state/labels keep you honest.
Settings that matter (and why)
- Spread Method Defines the “mispricing” you care about.
- Correlation Period Longer = steadier regime read, shorter = snappier to regime change.
- Z-Score Period The window that defines “normal” for the spread; it sets the yardstick.
- Use Percentage Returns Normalizes series when using return-based logic; keep on for mixed-scale assets.
- Entry / Exit Thresholds Set your stretch and your target reversion zone. Wider entries = rarer but stronger signals.
- Minimum Correlation The gatekeeper. Raising it favors quality over quantity.
Choosing pairs (practical cheat sheet)
- Same family: two index ETFs, two oil-linked names, two gold miners, two L1 tokens.
- Hedge & proxy: stock vs. sector ETF, BTC vs. BTC index, WTI vs. energy ETF.
- Cross-venue or cross-listing: instruments that are functionally the same exposure but price differently intraday.
Reading the cues like a pro
- Divergence shape: The yellow normalized spread helps you see rhythm fast spike and snap-back versus slow grind.
- Corr-first discipline: Don’t fight the “Min Correlation” line. Good pairs trading starts with a relationship you can trust.
- Exit humility: When Z re-centers, let the EXIT do its job. The edge is the journey to the mean, not overstaying it.
Frequently asked (quick answers)
- “Long/Short means what exactly?”LONG = long the chart symbol and short the pair symbol.
SHORT = short the chart symbol and long the pair symbol.
- “Do I need same price scales?” No. The spread methods normalize in different ways; choose the one that fits your use case (log/ratio are great for mixed scales).
- “What if correlation falls mid-trade?” The scanner will neutralize the state and print EXIT. Relationship first; trade second.
Field notes & patterns
- Snap-back days: After a one-sided session, return-difference spreads often flag cleaner intraday mean reversions.
- Macro rotations: Ratio spreads shine during sector re-weights (e.g., value vs. growth ETFs); look for steady corr + elevated |Z|.
- Event bleed-through: If one symbol reacts to news and its partner lags, Z often flags a high-quality, short-horizon re-centering.
Display controls at a glance
- Show Statistics Table Live state & key numbers, top-right.
- Show Analysis Table Context/risk read, bottom-right.
- Show Correlation / Spread / Z-Score Toggle the sub-charts you want visible.
- Show Entry/Exit Signals Turn markers on/off as needed.
- Coloring Adjust Long/Short/Neutral and correlation line colors to match your theme.
Alerts (ready to route to your workflow)
- Pairs Long Entry Z falls through the long threshold with correlation above minimum.
- Pairs Short Entry Z rises through the short threshold with correlation above minimum.
- Pairs Trade Exit Z returns to neutral or the relationship fails your correlation floor.
- Correlation Breakdown Rolling correlation crosses your minimum; relationship caution.
Final notes
The scanner is designed to keep you systematic: require relationship (correlation), quantify dislocation (Z-Score), act when stretched, stand down when it normalizes or the relationship degrades. It’s a full, visual loop for relative-value trading that stays out of your way when it should and gets loud only when the numbers line up.
สคริปต์โอเพนซอร์ซ
ด้วยเจตนารมณ์หลักของ TradingView ผู้สร้างสคริปต์นี้ได้ทำให้เป็นโอเพนซอร์ส เพื่อให้เทรดเดอร์สามารถตรวจสอบและยืนยันฟังก์ชันการทำงานของมันได้ ขอชื่นชมผู้เขียน! แม้ว่าคุณจะใช้งานได้ฟรี แต่โปรดจำไว้ว่าการเผยแพร่โค้ดซ้ำจะต้องเป็นไปตาม กฎระเบียบการใช้งาน ของเรา
Check out whop.com/signals-suite for Access to Invite Only Scripts!
คำจำกัดสิทธิ์ความรับผิดชอบ
ข้อมูลและบทความไม่ได้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อก่อให้เกิดกิจกรรมทางการเงิน, การลงทุน, การซื้อขาย, ข้อเสนอแนะ หรือคำแนะนำประเภทอื่น ๆ ที่ให้หรือรับรองโดย TradingView อ่านเพิ่มเติมใน ข้อกำหนดการใช้งาน
สคริปต์โอเพนซอร์ซ
ด้วยเจตนารมณ์หลักของ TradingView ผู้สร้างสคริปต์นี้ได้ทำให้เป็นโอเพนซอร์ส เพื่อให้เทรดเดอร์สามารถตรวจสอบและยืนยันฟังก์ชันการทำงานของมันได้ ขอชื่นชมผู้เขียน! แม้ว่าคุณจะใช้งานได้ฟรี แต่โปรดจำไว้ว่าการเผยแพร่โค้ดซ้ำจะต้องเป็นไปตาม กฎระเบียบการใช้งาน ของเรา
Check out whop.com/signals-suite for Access to Invite Only Scripts!
คำจำกัดสิทธิ์ความรับผิดชอบ
ข้อมูลและบทความไม่ได้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อก่อให้เกิดกิจกรรมทางการเงิน, การลงทุน, การซื้อขาย, ข้อเสนอแนะ หรือคำแนะนำประเภทอื่น ๆ ที่ให้หรือรับรองโดย TradingView อ่านเพิ่มเติมใน ข้อกำหนดการใช้งาน